Key Takeaways
- Zero-Crossing Factor: AC current naturally extinguishes arcs at zero-crossings (100-120 times/sec), while DC current sustains arcs continuously.
- Design Differences: DC isolators require magnetic blow-out coils and deep arc chutes, making them physically larger and more expensive than AC versions.
- Voltage Derating: Using an AC isolator for DC applications results in a significant drop in voltage capacity (e.g., 690V AC → ~220V DC).
- Safety Rule: Never use an AC-rated isolator for DC systems like Solar PV or Battery Storage to prevent fire hazards and contact welding.
The maintenance technician flips the isolator switch open. 600 volts, 32 amps. Routine lockout procedure for a rooftop solar array.
Except the switch wasn’t rated for DC.
Inside the housing, an arc forms between the separating contacts—a brilliant, sustained plasma bridge conducting 600V DC through ionized air. In an AC system, this arc would extinguish naturally within 10 milliseconds, snuffed out at the next current zero-crossing. But DC current has no zero-crossings. The arc sustains. The contacts begin to erode. Temperature climbs. Within seconds, the isolator that was supposed to provide safe disconnection has become a continuous high-voltage conductor, exactly when you need it isolated most.
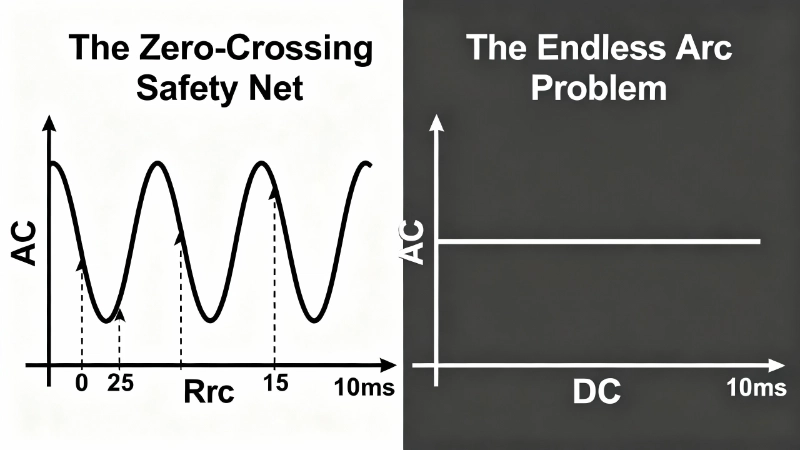
That’s “The Zero-Crossing Safety Net”—AC has it, DC doesn’t. And it changes everything about how isolator switches must be designed, rated, and selected.
What Are Isolator Switches?
An isolator switch (also called a disconnect switch or switch-disconnector) is a mechanical switching device designed to isolate an electrical circuit from its power source, ensuring safe maintenance and repair. Governed by IEC 60947-3:2020 for low-voltage switchgear (up to 1000V AC and 1500V DC), isolator switches provide visible disconnection—a physical gap you can see or verify—between live conductors and downstream equipment.
Unlike circuit breakers, isolators are not designed to interrupt fault currents under load. They’re maintenance disconnects. You open them when the circuit is de-energized or carrying minimal load, creating a safe isolation point for work downstream. Most isolators include a lockout mechanism (padlock hasp or lockable handle) for LOTO (Lockout/Tagout) compliance.
Here’s what makes isolator selection critical: the physics of arc interruption—what happens in the microseconds after you open the switch—is fundamentally different for AC vs DC. An isolator adequate for AC service may be completely inadequate (and dangerous) for DC service, even at lower voltage. The rating plate might say “690V,” but that’s 690V AC. Use it on a 600V DC solar string? You’ve just created a potential arc flash hazard.
This isn’t a minor technical detail or a conservative safety margin. It’s physics. And understanding why requires looking at what happens inside every switch when contacts separate under voltage.
Pro-Tip #1: Never use an AC-rated isolator for DC applications unless it has explicit DC voltage/current ratings on its datasheet. An isolator rated 690V AC typically has DC capacity of only 220-250V DC—less than a 4-panel solar string at open circuit.
The Arc Extinction Problem: Why DC Is Different
When you open any switch under voltage, an arc forms. It’s unavoidable. As the contacts separate, the gap between them is still small enough—micrometers, then millimeters—that voltage ionizes the air, creating a conducting plasma channel. Current continues to flow through this arc even though the mechanical contacts are no longer touching.
For the switch to truly isolate the circuit, this arc must be extinguished. And here’s where AC and DC diverge completely.
AC: The Natural Zero-Crossing
Alternating current, as its name suggests, alternates. A 50 Hz AC system crosses zero voltage/current 100 times per second. A 60 Hz system crosses zero 120 times per second. Every 8.33 milliseconds (60 Hz) or 10 milliseconds (50 Hz), the current flow reverses direction—and passes through zero.
At current zero-crossing, there’s no energy sustaining the arc. The plasma de-ionizes. The arc extinguishes. If the contacts have separated far enough by the next half-cycle, the gap’s dielectric strength (its ability to withstand voltage without re-ignition) exceeds the system voltage. The arc doesn’t re-strike. Isolation is achieved.
This is “The Zero-Crossing Safety Net.” AC isolators can rely on this natural interruption. Their contact design, gap distance, and arc chamber geometry only need to ensure the arc doesn’t re-strike after the next zero-crossing. It’s a relatively forgiving design problem.
DC: The Endless Arc Problem
Direct current has no zero-crossings. Ever. A 600V DC solar string delivers 600 volts continuously. When the isolator contacts separate and an arc forms, that arc is sustained by continuous energy. There’s no natural interruption point. The arc will continue indefinitely until one of three things happens:
- The contact gap becomes large enough that even the arc can’t bridge it (requiring much larger physical separation than AC)
- The arc is mechanically stretched, cooled, and blown out using magnetic fields and arc chutes
- The contacts weld together from sustained heating, defeating the entire purpose of isolation
Option 3 is what happens when you use an AC-rated isolator in DC service. The contact separation speed and gap distance that work fine for AC—because the next zero-crossing arrives in 10 milliseconds—are insufficient for DC. The arc sustains. Contact erosion accelerates. In the worst case, contacts weld, and you lose isolation entirely.
Pro-Tip #2: AC current crosses zero 100 times per second (50 Hz) or 120 times (60 Hz)—each zero-crossing is an opportunity for the arc to extinguish naturally. DC current never crosses zero. This isn’t a minor difference—it’s why DC isolators need magnetic blow-out coils and deep arc chutes that AC isolators don’t.
DC Isolator Design: The Arc Chamber Warrior
Because DC arcs won’t self-extinguish, DC isolators must force extinction through aggressive mechanical means. This is “The Arc Chamber Warrior”—a DC isolator is designed for battle.
Magnetic Blow-Out Coils
Most DC isolators incorporate magnetic blow-out coils or permanent magnets positioned near the contacts. When an arc forms, the magnetic field interacts with the arc current (which is a moving charge), producing a Lorentz force that pushes the arc away from the contacts and into the arc extinction chamber.
Think of it as a magnetic hand that physically shoves the arc away from where it wants to stay. The faster and further you move the arc, the more it cools and stretches, until it can no longer sustain itself.
Arc Chutes (Splitter Plates)
Once the arc is blown into the arc chamber, it encounters arc chutes—arrays of metal plates (often copper) that split the arc into multiple shorter segments. Each segment has its own voltage drop. When the total voltage drop across all segments exceeds the system voltage, the arc can no longer sustain. It collapses.
DC isolators use deeper, more aggressive arc chute designs than AC isolators because they can’t rely on current zero-crossings. The arc must be forcibly extinguished at full current, every time.
High-Silver Contact Materials
DC arcs are brutal on contacts. Sustained arcing at full voltage causes rapid erosion and heating. To withstand this, DC isolators use contact materials with higher silver content (often silver-tungsten or silver-nickel alloys) that resist welding and erosion better than the copper or brass contacts common in AC isolators.
The result? A DC isolator rated for 1000V DC at 32A is physically larger, heavier, more complex, and costs 2-3× more than a similarly rated AC isolator. This isn’t arbitrary pricing—it’s the engineering cost of forcing arc extinction without a zero-crossing.
Pro-Tip #3: For photovoltaic systems, always verify the isolator’s DC voltage rating exceeds your string’s maximum open-circuit voltage (Voc) at lowest expected temperature. A 10-panel string of 400W modules can reach 500-600V DC at -10°C—exceeding many “DC-capable” isolators. Also, refer to our guide on Connection of DC Isolators for safe wiring practices.
AC Isolator Design: Riding the Zero-Crossing
AC isolators are, by comparison, simple. They don’t need magnetic blow-out coils (though some include them for faster interruption). They don’t need deep arc chutes. They don’t need exotic contact materials.
Why? Because the zero-crossing does most of the work. The AC isolator’s job isn’t to forcibly extinguish the arc—it’s to ensure the arc doesn’t re-strike after the natural zero-crossing interruption.
- Sufficient gap distance: Typically 3-6mm for low-voltage AC, depending on voltage and pollution degree
- Basic arc containment: Simple insulating barriers to prevent arc tracking across surfaces
That’s it. AC isolators rely on the waveform to do the heavy lifting. The mechanical design just has to keep up. For specific applications like 3-phase motors, check our Complete Guide to 3-Phase Isolator Switch.

The Voltage Derating Penalty
Here’s a surprise that catches many engineers: if you must use an AC-rated isolator for DC (which you shouldn’t, but hypothetically), its DC voltage capacity is dramatically lower than its AC rating. This is “The Voltage Derating Penalty.”
A typical pattern:
- 690V AC rated → approximately 220-250V DC capacity
- 400V AC rated → approximately 150-180V DC capacity
- 230V AC rated → approximately 80-110V DC capacity
Why such severe derating? Because DC arc voltage is fundamentally different from AC arc voltage. Manufacturers account for this by dramatically reducing the DC voltage rating.
For solar PV applications, this is “The PV String Trap.” A common 400W solar panel has an open-circuit voltage (Voc) of approximately 48-50V at STC. String 10 panels together: 480-500V. But Voc increases at lower temperatures. A 400V AC isolator with a 180V DC rating? Completely inadequate.
Pro-Tip #4: Isolators are designed for no-load or minimal-load switching—they’re maintenance disconnects, not overcurrent protection. For environments requiring weather protection, ensure you understand IP ratings for isolator switches.

DC vs AC Isolator: Key Specifications Compared
| Specification | AC Isolator | DC Isolator |
|---|---|---|
| Arc Extinction Mechanism | Natural current zero-crossing (100-120 times/sec) | Forced mechanical extinction (magnetic blow-out + arc chutes) |
| Contact Gap Required | 3-6mm (varies by voltage) | 8-15mm (larger gap for same voltage) |
| Arc Chute Design | Minimal or none | Deep splitter plates, aggressive geometry |
| Magnetic Blow-Out | Optional (for fast interruption) | Mandatory (permanent magnets or coils) |
| Contact Material | Copper, brass, standard alloys | High silver content (Ag-W, Ag-Ni alloys) |
| Voltage Rating Example | 690V AC | 1000V DC or 1500V DC |
| Current Rating Example | 32A, 63A, 125A typical | 16A-1600A (wider range for PV/ESS) |
| Typical Applications | Motor control, HVAC, industrial AC distribution | Solar PV, battery storage, EV charging, DC microgrids |
| Standards | IEC 60947-3:2020 (AC utilization categories) | IEC 60947-3:2020 (DC utilization categories: DC-21B, DC-PV2) |
| Size & Weight | Compact, lightweight | Larger, heavier (2-3× size for same current rating) |
| Cost | Lower (baseline) | 2-3× more expensive |
| Arc Duration on Opening | <10ms (to next zero-crossing) | Continuous until mechanically extinguished |
Key Takeaway: The “2-3× cost penalty” for DC isolators isn’t price gouging—it reflects the fundamental physics tax of extinguishing arcs without zero-crossings.
When to Use DC vs AC Isolators
The decision isn’t about preference or cost optimization—it’s about matching the isolator’s arc extinction capability to your system’s current type.
Use DC Isolators For:
1. Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Systems
Every solar array DC string requires isolation between the array and the inverter. String voltages commonly reach 600-1000V DC. Look for IEC 60947-3 DC-PV2 utilization category specifically designed for PV switching duty. Refer to our guide on Solar Combiner Box Voltage Ratings for more details.
2. Battery Energy Storage Systems (ESS)
Battery banks operate at DC voltages ranging from 48V to 800V+. Isolation is required between battery modules and inverters.
3. EV Charging Infrastructure
DC fast chargers deliver 400-800V DC directly to vehicle batteries.
4. DC Microgrids and Data Centers
Data centers increasingly use 380V DC distribution to reduce conversion losses.
5. Marine and Rail DC Distribution
Ships and trains have used DC distribution (24V, 48V, 110V, 750V) for decades.
Use AC Isolators For:
1. Motor Control Circuits
Isolation for AC induction motors, HVAC systems, and pumps.
2. Building AC Distribution
Isolation for lighting panels and general building loads.
3. Industrial AC Control Panels
Machine control cabinets with AC contactors and PLCs.
The Critical Rule
If your system voltage is DC—even 48V DC—use a DC-rated isolator. The arc physics don’t care about voltage level; they care about waveform type. A 48V DC arc can still sustain and cause contact welding in an AC-only switch.

Selection Guide: 4-Step Method for DC Isolators
Step 1: Calculate Maximum System Voltage
For Solar PV: Calculate string Voc at lowest expected ambient temperature. Voc increases approximately 0.3-0.4% per °C below 25°C.
- Example: 10-panel string, Voc = 49V/panel at STC. At -10°C: 49V × 1.14 (temp factor) × 10 panels = 559V DC minimum isolator rating
Pro-Tip: Always spec isolator voltage rating at least 20% above calculated maximum system voltage for safety margin.
Step 2: Determine Current Rating
For Solar PV: Use string short-circuit current (Isc) × 1.25 safety factor.
Step 3: Verify Utilization Category
Check the datasheet for IEC 60947-3 utilization category: DC-21B for general DC circuits, DC-PV2 specifically for photovoltaic DC switching.
Step 4: Confirm Short-Circuit Rating (If Applicable)
Most isolators are designed for no-load or minimal-load switching. For regular load switching or fault interruption, specify a DC circuit breaker instead.
Pro-Tip #5: DC isolators cost 2-3× more than equivalent AC isolators because they require fundamentally different contact materials, magnetic blow-out systems, and deep arc extinction chambers.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use an AC isolator for DC applications?
No, generally you cannot. AC isolators rely on the “zero-crossing” of alternating current to extinguish electrical arcs. DC current does not have a zero-crossing, meaning arcs can sustain indefinitely in an AC switch, leading to overheating, fire, and contact welding.
Why are DC isolators bigger than AC isolators?
DC isolators require larger internal components, such as magnetic blow-out coils and deeper arc chutes (splitter plates), to mechanically force the extinction of the arc. They also require wider contact gaps to prevent the arc from restriking.
What is the difference between a DC isolator and a DC circuit breaker?
A DC isolator is designed primarily for maintenance disconnection (isolating the circuit) and is usually operated off-load. A DC circuit breaker provides automatic protection against overloads and short circuits and is designed to interrupt fault currents under load.
Conclusion: Physics Isn’t Optional
The difference between DC and AC isolator switches isn’t a matter of ratings, cost, or preference. It’s physics.
AC isolators rely on “The Zero-Crossing Safety Net”. DC isolators face “The Endless Arc Problem”. The arc will sustain indefinitely unless the switch forces extinction through magnetic blow-out coils and deep arc chutes.
When you spec an isolator for a solar PV string or battery storage, you’re selecting an arc extinction system. Use the wrong one, and you risk sustained arcing and fire. The rule is simple: If your voltage is DC, use a DC-rated isolator.
Physics isn’t negotiable. Choose accordingly.
Need help selecting DC isolators for your solar PV or battery storage project? Contact our application engineering team for technical guidance on IEC 60947-3 compliant DC switching solutions.






