I. Introduction
A. Definition of Fire Alarm Relay Modules
Fire alarm relay modules are electronic devices that serve as intermediaries between a fire alarm control panel and various connected devices within a fire detection system. They function as switches, enabling the control panel to activate or deactivate components such as strobe lights, sirens, sprinkler systems, and ventilation systems during a fire event. By facilitating communication between the control panel and these devices, relay modules ensure a coordinated response to emergencies.
B. Importance in Fire Safety Systems
Fire Alarm System
The significance of fire alarm relay modules in fire safety systems cannot be overstated. They enhance the overall efficiency and effectiveness of fire detection systems through several key functions:
- Device Activation and Deactivation: Relay modules allow for the precise control of multiple devices, ensuring that alarms and safety measures are activated promptly when needed.
- Integration with Other Systems: They enable the integration of fire alarm systems with other building management systems, such as HVAC and security systems. This integration is crucial for managing smoke control and ensuring safe egress during emergencies.
- Fault Isolation: Relay modules help isolate faults within the system by allowing malfunctioning devices to be disconnected without disrupting overall system functionality. This capability is vital for maintaining operational integrity during a fire incident.
- Emergency Power Management: In cases of power outages, relay modules can manage emergency power sources to ensure that critical systems remain operational.
- Customization and Flexibility: The adaptability of relay modules allows for tailored configurations based on specific building layouts and safety requirements, enhancing their effectiveness in diverse environments.
II. Understanding Fire Alarm Relay Modules
A. Basic function and operation
Fire alarm relay modules are essential components of fire alarm systems, acting as switches that control the activation and deactivation of various electrical devices during a fire emergency. When the fire alarm system detects a potential threat, it sends a small electrical signal to the relay module. This signal activates the relay, which then closes a set of contacts to complete a circuit, allowing a larger current from an external power source to flow to devices such as sprinkler systems, alarms, or smoke exhaust systems. This mechanism enables the fire alarm system to manage multiple devices efficiently without overloading the system, ensuring a rapid response in emergencies.
B. Types of relay modules
There are several types of relay modules used in fire alarm systems, each serving specific functions:
- Control Relay Modules: These modules output voltage to activate alarms or other signaling devices when triggered by the fire alarm control panel. They are commonly used to turn on horn/strobes and other notification appliances.
- Monitor Relay Modules: These are designed to monitor specific circuits or devices, such as pull stations or smoke detectors, and report their status back to the control panel. They can help integrate older systems into modern addressable systems.
- Output Relay Modules: Often referred to simply as relay modules, these can switch larger loads and are used for controlling external devices like door holders or HVAC systems during an emergency.
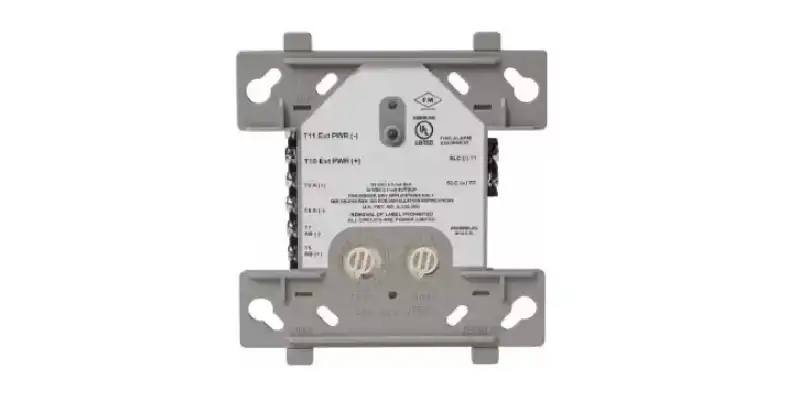
C. Key components
Fire alarm relay modules consist of several key components that enable their functionality:
- Input Connections: These interface with the fire alarm control panel, receiving signals that indicate when a fire alarm has been triggered.
- Output Terminals: These connect to external devices that need to be controlled, allowing the relay module to manage power delivery based on the input signal.
- Relay Contacts: The internal mechanism that opens or closes circuits based on the received signals. The contacts can be configured in various forms (e.g., Form C) to suit different applications.
- LED Indicators: Many relay modules include LED lights that provide visual feedback on their operational status—typically indicating whether they are in a normal state or have been activated due to an alarm condition.
III. Benefits of Fire Alarm Relay Modules
A. Improved System Integration
Fire alarm relay modules facilitate seamless integration between fire detection systems and other building management systems, such as HVAC and security systems. This integration allows for coordinated responses during emergencies, such as controlling airflow to prevent smoke spread or locking down areas to ensure safe egress. By connecting various systems, relay modules enhance the overall safety and efficiency of fire protection measures, ensuring that all components work together effectively in critical situations.
B. Enhanced Control and Monitoring
Relay modules provide enhanced control over connected devices, allowing for precise activation and deactivation based on real-time conditions. They enable fire alarm systems to manage multiple outputs simultaneously, such as activating alarms, strobe lights, and sprinkler systems when a fire is detected. Additionally, many modern relay modules offer remote monitoring capabilities, allowing system operators to oversee performance and respond quickly to any issues or alarms from a centralized location.
C. Increased Reliability
The reliability of fire alarm systems is significantly bolstered by the use of relay modules. These components are designed with built-in supervision and diagnostics that alert operators to potential faults, thus preventing system failures during emergencies. By isolating malfunctioning devices without compromising the entire system’s functionality, relay modules ensure that the fire detection system remains operational even in the event of component failures. This reliability is crucial for maintaining safety standards and compliance with regulations like NFPA 72.
D. Cost-effectiveness
Investing in fire alarm relay modules can lead to long-term cost savings for building owners and operators. By improving system integration and reliability, these modules reduce the likelihood of costly false alarms and unnecessary service calls. Additionally, their ability to manage multiple devices efficiently can lower installation and maintenance costs by minimizing the complexity of wiring and control systems. Overall, the use of relay modules contributes to a more streamlined fire safety solution that can adapt to changing needs without incurring significant additional expenses.
IV. Applications of Fire Alarm Relay Modules
A. Residential Buildings
In residential settings, fire alarm relay modules enhance safety by integrating with smoke detectors and alarm systems to manage notifications and emergency responses. These modules can activate interconnected alarms throughout the home, ensuring that alerts are heard in all areas. Additionally, they can control systems like emergency lighting or door locks, facilitating safe egress during a fire event. This integration is particularly beneficial in multi-story homes or apartment complexes where rapid communication is crucial.
B. Commercial Structures
Fire alarm relay modules play a vital role in commercial buildings by connecting various fire detection devices and ensuring compliance with safety regulations. They enable the integration of fire alarms with building management systems, allowing for automatic door unlocking during emergencies and the activation of fire suppression systems. Moreover, relay modules help minimize false alarms and enhance the overall reliability of fire safety measures in environments such as offices, retail spaces, and warehouses.
C. Industrial Facilities
In industrial settings, the application of fire alarm relay modules is critical due to the presence of hazardous materials and complex machinery. These modules can control ventilation systems to manage smoke and heat during a fire, activate alarms across large facilities, and interface with other safety systems like sprinkler controls. Their ability to monitor multiple devices simultaneously ensures that any fire threat is addressed promptly, thereby protecting both personnel and property from potential disasters.
D. Healthcare Institutions
Healthcare institutions utilize fire alarm relay modules to ensure the safety of patients and staff in environments where quick evacuation may be challenging. These modules can integrate with nurse call systems and other critical infrastructure to provide timely alerts during a fire emergency. They also facilitate the control of smoke barriers and ventilation systems to maintain safe air quality within medical facilities. The reliability and responsiveness of these modules are essential for protecting vulnerable populations in hospitals and nursing homes.
V. How Fire Alarm Relay Modules Work
A. Signal Reception and Transmission
Fire alarm relay modules operate by receiving a low-voltage signal from the fire alarm control panel (FACP) when a fire alarm is triggered. This signal indicates that a fire event has been detected, prompting the relay module to respond. The relay module is designed to interpret this signal, which can be a small amount of electricity, and then transmit it to connected devices. For instance, when a smoke detector senses smoke, it sends an activation signal to the relay module, which then activates its output contacts to control external devices like alarms or sprinkler systems.
B. Activation of Connected Devices
Once the relay module receives the activation signal, it closes its internal contacts to complete an electrical circuit. This action allows a larger current from an external power source to flow to connected devices, such as strobe lights, sirens, or fire suppression systems. The relay can be configured for different operational modes—such as continuous or pulse output—depending on the specific requirements of the application. For example, in pulse mode, the relay may activate a device for a brief period before automatically returning to its original state. This functionality is crucial for ensuring that emergency devices operate effectively during a fire event.
C. Interfacing with Other Building Systems
Fire alarm relay modules also serve as critical interfaces between fire detection systems and other building management systems (BMS), such as HVAC or access control systems. By integrating with these systems, relay modules enhance overall safety and operational efficiency. For instance, they can manage airflow during a fire by controlling ventilation systems to prevent smoke spread or automatically unlock doors to facilitate safe evacuation. This interoperability not only improves response times but also ensures that all building systems work in concert during emergencies, maximizing occupant safety and minimizing property damage.
VI. Choosing the Right Fire Alarm Relay Module
A. Compatibility Considerations
When selecting a fire alarm relay module, compatibility with existing fire alarm control panels and devices is paramount. Ensure that the relay module is designed to work with your specific fire alarm system, such as the Silent Knight IFP-series or other brands like Aico. Many modules, like the Farenhyt Addressable Relay Module, feature unique signaling line circuit (SLC) loop addresses, which must match the control panel’s requirements for effective communication and operation. Additionally, consider whether the module supports both normally open and normally closed applications, as this flexibility can be crucial for various installations.
B. Capacity and Expandability
Evaluate the capacity of the relay module to handle the number of devices you plan to connect. Modules vary in terms of the number of relays they offer; for example, some can feature multiple Form-C relays which allow for extensive control options across different systems. Furthermore, consider the expandability of the module. Some systems allow for additional modules to be added as needed, which is beneficial for future upgrades or expansions without requiring a complete system overhaul. Ensure that any chosen module can accommodate your current and anticipated needs.
C. Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with local and national fire safety regulations is critical when choosing fire alarm relay modules. Look for modules that have certifications from recognized standards organizations, such as Underwriters Laboratories (UL) or equivalent bodies in your region. These certifications ensure that the module meets stringent safety and performance criteria. Additionally, check if the relay module complies with relevant codes like NFPA 72, which governs fire alarm systems in the United States. Adhering to these regulations not only enhances safety but also helps avoid potential legal liabilities associated with non-compliance.
VII. Installation and Maintenance
A. Best Practices for Installation
- Placement and Wiring: Fire alarm relay modules should be strategically located to minimize wiring distance and ensure optimal coverage. This placement enhances signal integrity and reduces installation complexity.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the relay module is compatible with the specific fire alarm system being installed, including voltage requirements and communication protocols. This step is crucial for effective operation.
- Adherence to Standards: Follow local fire codes and regulations, such as CAN/ULC-S524 in Canada, which outlines installation practices for fire alarm systems. This includes proper mounting heights (e.g., modules should be mounted no higher than 1800 mm above the finished floor) and ensuring accessibility for maintenance.
- Professional Installation: Engage qualified professionals for installation to guarantee compliance with safety standards and optimal functionality of the relay modules.
B. Regular Testing and Maintenance Requirements
- Routine Testing: Conduct regular tests to verify the functionality of fire alarm relay modules and associated devices. This includes checking that the relay changes state correctly when activated by the fire alarm control panel (FACP) and that connected devices respond as intended.
- Scheduled Maintenance: Follow manufacturer recommendations for scheduled maintenance to prolong the lifespan of relay modules. This may include cleaning, inspecting connections, and replacing any worn components.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed records of all tests and maintenance activities, including dates, findings, and corrective actions taken. This documentation is essential for compliance with regulatory requirements and for future reference.
C. Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Signal Failure: If a relay module does not activate connected devices, check for wiring faults or loose connections between the module and the FACP or output devices. Ensure that power is supplied correctly to the module.
- False Alarms: Investigate potential causes of false alarms, such as environmental factors or malfunctioning sensors that may be incorrectly triggering the relay module. Adjustments or replacements may be necessary to resolve these issues.
- LED Indicators: Many relay modules feature LED indicators that provide visual feedback on their operational status. If an LED is not illuminated when it should be, this may indicate a malfunction or power issue that requires immediate attention.
- Consult Manufacturer Guidelines: Always refer to the manufacturer’s troubleshooting guidelines for specific issues related to their products, as they may offer tailored solutions based on design specifications.
VIII. Manufacturers of Fire Alarm Relay Modules
Honeywell
- Website: honeywell.com
- Honeywell offers the Farenhyt Addressable Relay Modules, which are designed for use with Silent Knight IFP-series fire alarm control panels. These modules feature multiple Form-C relays and flexible programming options.
Aico
- Website: aico.co.uk
- Aico’s Ei128R Hard Wired Relay Module is mains powered and connects with alarm systems to trigger external devices like strobe lights and telecare devices. It is compatible with various Aico alarm series.
C-Tec
- Website: discountfiresupplies.co.uk
- C-Tec offers a range of relay modules suitable for 24V fire alarm systems, including isolatable relays and auxiliary device isolators.
Fike
- Website: fike.com
- Fike’s Cheetah Xi system utilizes intelligent relay modules that communicate peer-to-peer, providing rapid response times and extensive programmability for fire safety applications.
IX. Conclusion
Choosing the right relay module, ensuring proper installation, and maintaining regular testing and maintenance schedules are essential for maximizing the benefits of these devices. As fire safety regulations become increasingly stringent, the role of relay modules in ensuring compliance and protecting lives and property will only grow in importance.
In conclusion, fire alarm relay modules represent a critical component in modern fire safety infrastructure, offering a blend of technological advancement, reliability, and adaptability that is essential for meeting the challenges of fire protection in the 21st century.
X. FAQs
A. What is the difference between conventional and addressable relay modules?
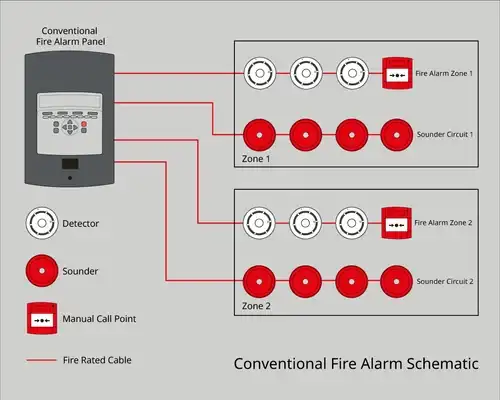
Conventional relay modules are part of older fire alarm systems where each device is connected to the control panel via separate wiring for each device or zone. This means that if an alarm is triggered, the panel indicates only the zone where the alarm occurred, requiring personnel to investigate further to find the exact source of the alarm. In contrast, addressable relay modules are part of more advanced systems where each device has a unique address on a single communication line. This allows the control panel to pinpoint the exact location of the alarm, providing more detailed information and improving response times during emergencies.
B. How often should Fire Alarm Relay Modules be tested?
Fire alarm relay modules should be tested at least once a year as part of a comprehensive fire safety plan. However, more frequent testing may be recommended based on local regulations or specific building requirements. Regular testing ensures that all components function correctly and that any faults can be identified and rectified promptly. Additionally, monthly checks of visual indicators (like LED lights) can help ensure that modules are operational.
C. Can Fire Alarm Relay Modules be retrofitted into existing systems?
Yes, fire alarm relay modules can often be retrofitted into existing systems, especially when upgrading from conventional to addressable systems. Many manufacturers offer monitor modules that allow older devices to become addressable without complete replacement. However, compatibility with existing components must be verified to ensure proper functionality and compliance with safety standards.
D. Are wireless Fire Alarm Relay Modules as reliable as wired ones?
Wireless fire alarm relay modules can be reliable but generally depend on the specific technology used and environmental factors. Wired modules typically offer greater reliability due to their consistent power supply and immunity to interference from physical obstructions or electronic devices. However, advancements in wireless technology have improved their reliability significantly, making them suitable for many applications, particularly in retrofitting scenarios where running new wires is impractical. Ultimately, the choice between wired and wireless should consider specific installation conditions, regulatory requirements, and system design.
Article Source:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fire_alarm_system
https://blog.dga.com/fire-relays-integrating-access-control-and-fire-systems